Donna May Lina with Agay Llanera
It’s been a little over a year since the Philippines reported its first COVID-19 case. Since then, our lives have drastically changed. To reduce the spread of the virus, we all had to learn the basic protocols: wash our hands, wear a mask, maintain physical distance. Guidelines were set out on international, national and barangay levels.
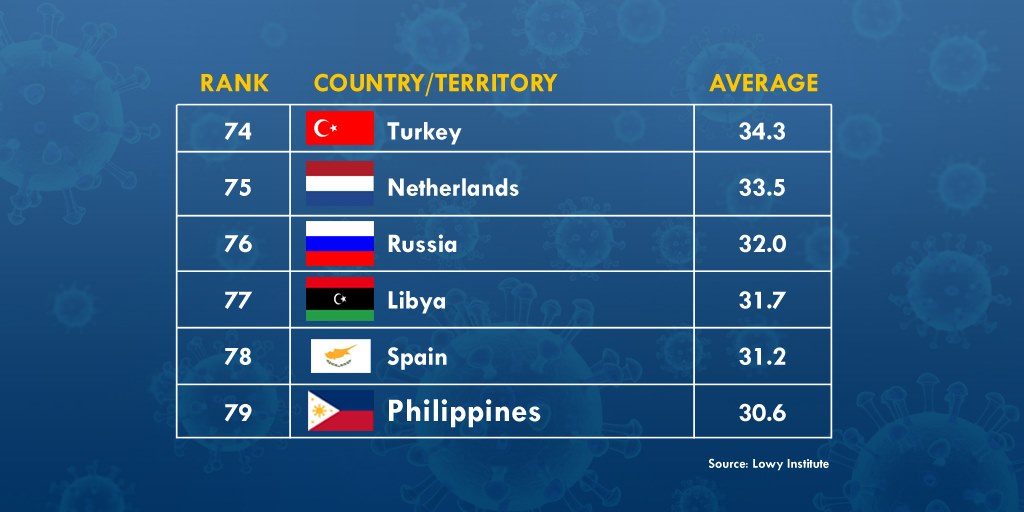
Just a few weeks ago, Lowy Institute, an Australian think-tank group, compared the effectiveness of the different countries’ pandemic responses. Criteria included the numbers of reported cases and deaths, tests conducted, and the rates of positive tests. On the list, the Philippines ranked 79th in terms of COVID-19 performance. Top countries that were able to control the virus were New Zealand (1st), Vietnam (2nd), Taiwan (3rd) and Singapore (13th).
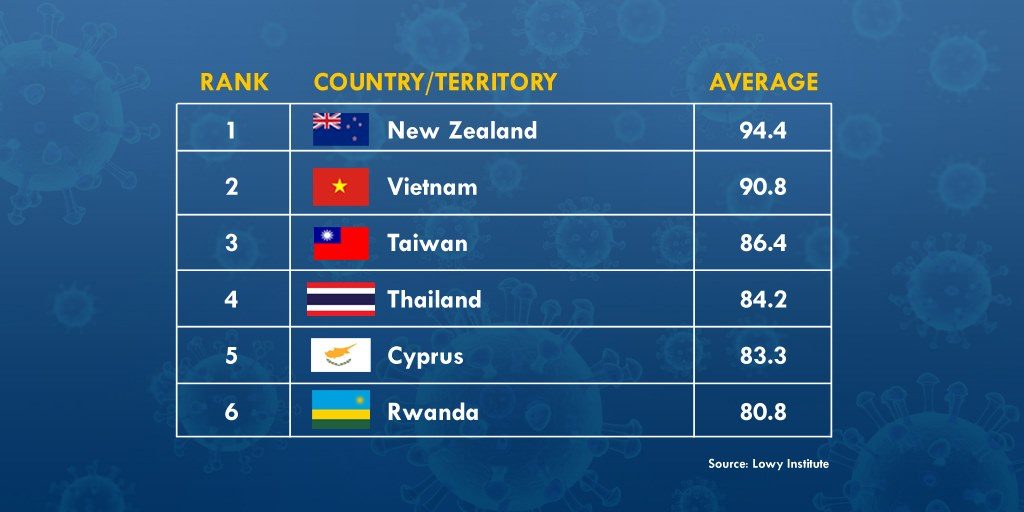
 (Source: Lowy Institute)
(Source: Lowy Institute)
What did they do right?
For one, these countries have very clear guidelines. The New Zealand government has created separate COVID-19 safety websites for specific audiences—the business and service sector, workers, and even for its construction industry. Taiwan has only seven pandemic-related deaths because of its tight entry restrictions. As early as February last year, travelers with Taiwanese mobile numbers have been utilizing the QR code system for health declarations. Even home quarantine and isolation monitoring are done via mobile phones; if a person left quarantine, his or her phone will alert authorities who will immediately verify the person’s location.
With clear guidelines come clear penalties. To compare how the Philippines compares with other countries in meting out fines for the simple safety protocol of wearing face masks, Panahon TV came up with this chart:
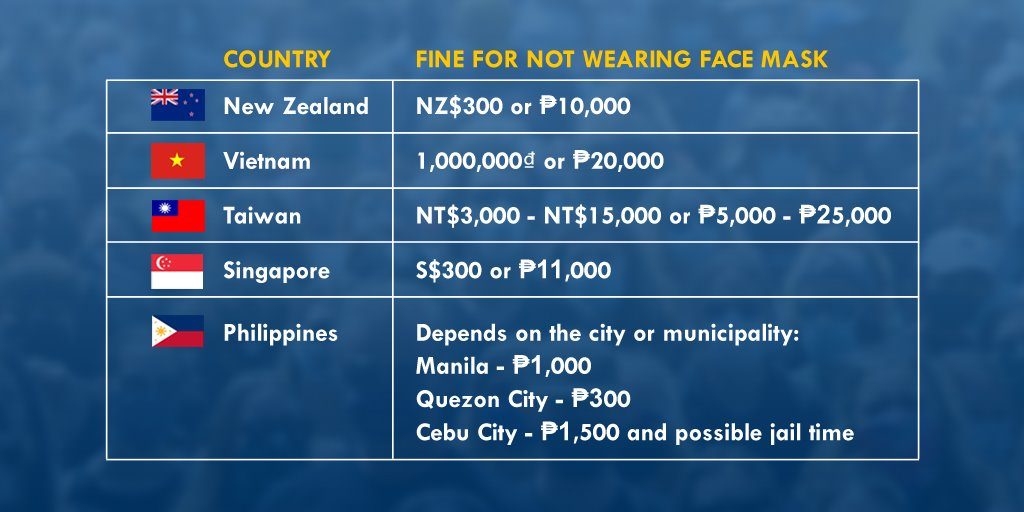
With local government units in our country having their own penalties, guidelines become confusing especially for travelers. A quick web search on sanctions for those failing to comply with COVID-19 safety protocols also revealed the following:
- New Zealand nips irresponsible behavior in the bud by imposing a fine of NZ$4,000 (₱14,000) for travelers who refuse to test for COVID-19. Violators can be held for 28 days.
- In Vietnam, those who escape quarantine sites, avoid quarantine measures, and fail to complete health declarations face criminal punishment.
- When an OFW left his room at a quarantine hotel in Taiwan for eight seconds, he was fined NT$100,000 (₱172,000).
- Those who fail to comply with Stay-Home Notice requirements in Singapore may be penalized up to S$10,000 (₱360,000) and/or imprisonment of up to six months.
- The farthest the Philippine government has gotten in this area is the mere suggestion of imposing community service and fines for quarantine violators. As of writing, no clear penalties have been drafted.
Factors that Contribute to Pandemic Response
Politics and location play a big role in the different pandemic responses across the globe. Vietnam and Taiwan are known for their disciplined citizens because they have always been challenged by threats of war. Due to geographical reasons, New Zealand has learned to be self-contained. A strict compliance with laws has always been the key component of Singapore’s governance.
Culturally, these countries have a more collectivist culture. Social psychologists define collectivism as a value that emphasizes interconnectedness, prioritizing a society’s goal and needs over those of the individual.
Interestingly enough, countries known for their individualistic cultures seem to have weaker pandemic responses, as listed by the Lowy Institute’s report. These include Sweden (37th), the UK ( 66th), Netherlands (75th) and the U.S. (94th).
A Centers for Disease Control and Prevention commentary observes how COVID-19 measures seem to focus more on individual risks, which lead to gaps in response. In order to curtail the global spread of the virus, messaging should promote cultural inclusivity. But instead of pitting one culture type against the other, the commentary suggests embracing “multicentric logics – individual, collective, and everything in between.” Different cultures and attitudes are factors in seeing how countries will be able to implement, comply, and continue to maintain safety guidelines to this date.
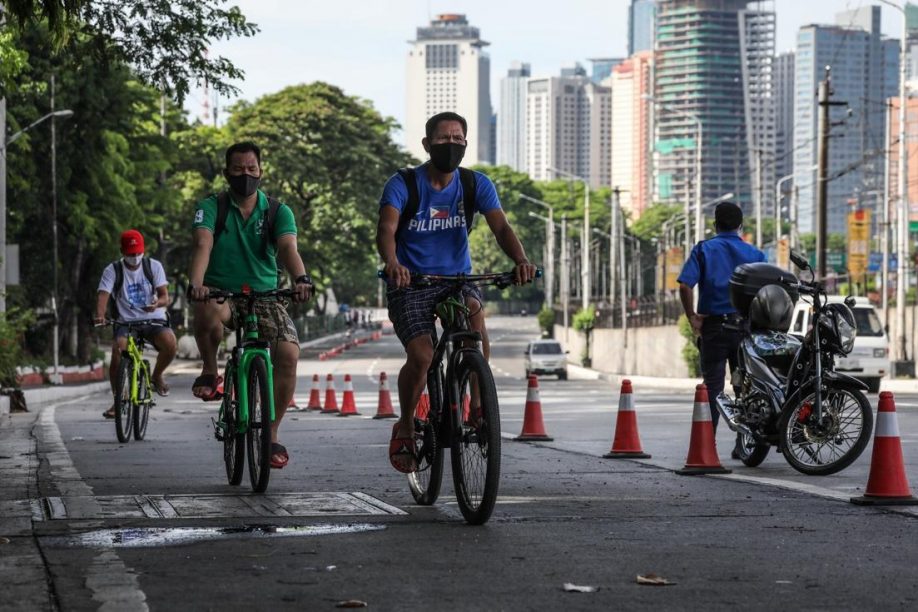 (photo by Jire Carreon)
(photo by Jire Carreon)
How will the pandemic end?
In an attempt to answer this question, the New York Times discussed how the 1918 Spanish flu virus, which killed as many as 100 million people worldwide, has simply lost steam, evolving into a still potentially fatal seasonal flu.
With the vaccine race “won” in round one by pharmaceutical companies like Moderna (U.S.) and AstraZeneca (UK), more than 108 million vaccine doses have been administered in 67 countries.
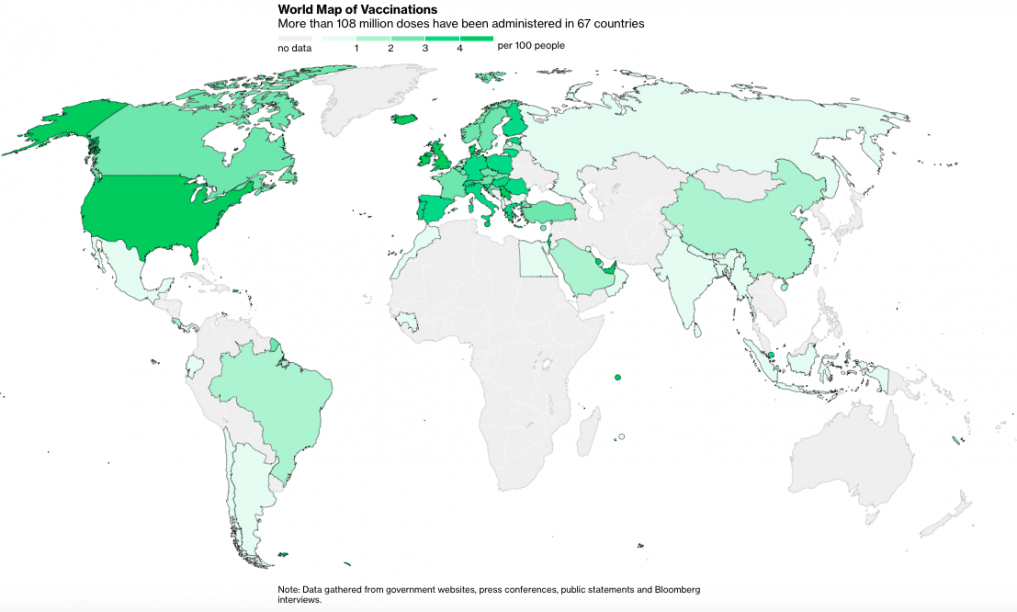 (Source: Bloomberg)
(Source: Bloomberg)
The vaccines were developed through collaborating scientists, were tested among selfless volunteers, and rolled out to countries’ frontliners and vulnerables depending on government strategy. Through modern technology and cooperation, vaccination has been conducted through Emergency Use Authorization, allowing the release of unregistered drugs and vaccines during a public health emergency. No other vaccine has been rolled out this fast.
But we will still need to work together and faster. The virus is mutating, and has evolved into variants from the UK, South Africa and Brazil, which are being closely monitored by health experts. Though vaccination seems to be the best solution in ending the pandemic, it doesn’t mean that the virus will magically disappear.
The Philippines is reported to receive the vaccines by the second quarter of this year. While we all wait for the vaccine rollout in our country, the best thing for us to do is to comply to safety standards.
The Philippine government has basic taglines for the people’s easy recall. Repetition has always been an effective communication tactic. There’s the Department of Public Work and Highway’s Build, Build, Build; and the Department of Agriculture’s Plant, Plant, Plant.
We should all then Comply, Comply, Comply to washing our hands. Comply, Comply, Comply to wearing face masks. Comply, Comply, Comply to maintaining physical distance. Comply, Comply, Comply to answering contact trace forms.
This may be easier said three times than done, but if we want our country to fare better, we must continue fighting the good fight despite quarantine and protocol fatigue. In this global crisis, there is no room for complacency, only repetitive compliance. Whether you’re privileged, careless, or downright indifferent, one thing is clear: the virus does not care.
Just after midnight on August 17, 1976, a magnitude 8 earthquake shook the areas around Moro Gulf in Mindanao, including Cotabato City. But the disaster did not stop there; less than 5 minutes later, a tsunami as high as 9 meters roared and swallowed 700 kilometers of coastline. When the sea ebbed to its peaceful state, around 8,000 had died from the combined effects of the earthquake and tsunami, with the latter accounting for 85% of deaths and 95% of those missing and never found. The event, now known as the 1976 Moro Gulf Earthquake, is recognized as the deadliest earthquake that ever hit the country.
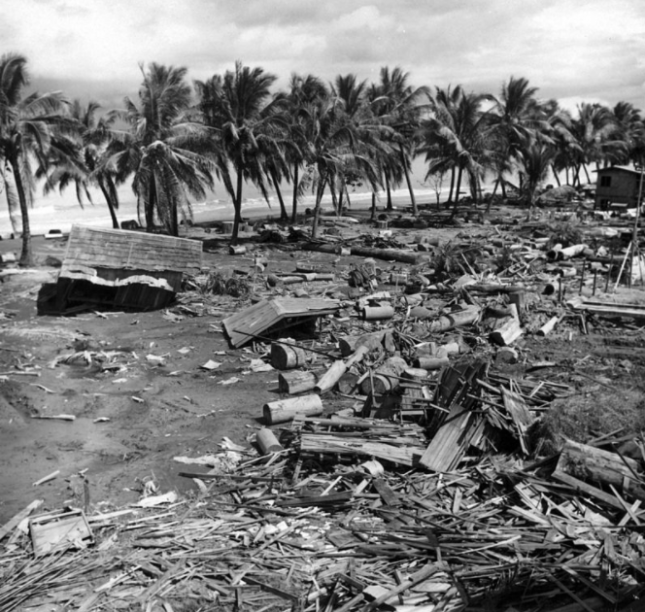 Devastation of the 1976 tsunami at Barangay Tibpuan in Lebak, Mindanao (Photo from Wikimedia Commons)
Devastation of the 1976 tsunami at Barangay Tibpuan in Lebak, Mindanao (Photo from Wikimedia Commons)
Almost two decades later on November 15, 1994, Mindoro was rocked by a magnitude 7.1 earthquake. Like what happened in Mindanao, majority of the 78 casualties of the Mindoro earthquake was due to the 8-meter high tsunami that occurred 5 minutes after the quake.
The truth is, though Filipinos are aware of devastating tsunami happening in other countries like Japan and Indonesia, they do not often associate these natural disasters in their homeland. But as past events indicate, deadly tsunami can occur locally. As Undersecretary of the Department of Science and Technology (DOST) for Disaster Risk Reduction-Climate Change Adaptation (DRR-CCA) and Officer-In-Charge of the Philippine Institute of Volcanology and Seismology (PHIVOLCS) put it, “Tsunami are very fast in the Philippines and we need to prepare for them.”

Tsunami 101
In observance of World Tsunami Awareness Day last November 5, PHIVOLCS organized an online press conference to spread the word about tsunami. Mostly generated by under-the-sea earthquakes, tsunami are characterized by a series of waves with heights of more than 5 meters. According to Solidum, such earthquakes can be triggered by underwater landslides, volcanic eruptions, and the more unlikely meteor impacts. These cause the seafloor to lift, causing the water it carries to rise.
There are two types of tsunami—the distant and local. Distant or far-field tsunami is generated outside the Philippines, mainly from countries bordering the Pacific Ocean like Chile, Alaska (U.S.) and Japan. With these events being monitored by The Pacific Tsunami Warning Center (PTWC), the Philippines has 1 to 24 hours of preparation before the tsunami’s arrival, depending on its origin.
But with local tsunami, lead time is cut down to a mere 2 to 10 minutes after the earthquake. “Preparedness is very important because rapid response is needed for locally-generated tsunami. The trenches are where the large earthquakes and tsunami can be generated, and we are only the country wherein trenches can be found on both sides. Hence, both sides of the country need to prepare for tsunami. Aside from that, the eastern side of the country faces the Pacific Ocean or the Pacific Ring of Fire where earthquakes and tsunami can also be generated,” said Solidum.
What PHIVOLCS is doing
Part of the Tsunami Risk Reduction Program of PHIVOLCS are the Tsunami Hazard Mapping and Modeling, and the Tsunami Hazard Risk Assessment, both of which aim to understand tsunami, manage their hazards and risks, and identify priority actions for response and recovery. To detect possible tsunami, PHIVOLCS set up its Monitoring and Detection Networks Development.
Aside from the 107 seismic stations that receive data for earthquakes and tsunami, there are also 29 real-time tide gauges all over the country. Through the hazards and risk-assessment software code REDAS, PHIVOLCS can evaluate potential earthquake hazards, create tsunami simulations, and predicting the number of affected people. “The total population exposed to tsunami would be close to 14 million,” said Solidum. “But they will not be affected at the same time. It would depend on where the tsunami would occur. In NCR, for example, the prone population would be around 2.4 million. And the next highest would be 1.6 million in Region VII, 1.2 million in Region VI— and in Region IXA, around 1 million.”
Meanwhile, HazardHunter Philippines, which is open for public use, can assess hazards depending on the user’s specific location. “HazardHunter can also give you a more detailed tsunami hazards assessment because it can provide you a map showing the different areas that will be affected by different tsunami heights. It is color coded, indicating areas prone to various tsunami heights.” Solidum appealed to the public to take advantage of the “Report a Disaster” website. Here, people can post pictures and videos of current risks and hazards in their areas, and describe disasters impacts, which can help the government’s risk and impact assessments.
 Screencap of “Report a Disaster” website
Screencap of “Report a Disaster” website
“In the Philippines, we use a simple tsunami information or warning scheme,” explained Solidum. “We will evacuate once the tsunami information is categorized as a tsunami warning. We expect a destructive tsunami of more than 1 meter and this would need immediate evacuation of coastal areas. Boats at sea are advised to say offshore — in deep waters.”
Shake, drop and roar
Because local tsunami can be very fast, people need to know its natural signs:
Shake – refers to a strong earthquake.
Drop – refers to the sea level receding fast.
Roar – refers to the unusual sound of the returning wave, which indicates a tsunami.
After an earthquake, Solidum recommends for people near the shore to immediately move to elevated ground inland, or take refuge in tall and strong buildings. “If they have not moved at all, once they hear the tsunami and there are unusual sounds, there might not be enough time. They really need to respond immediately,” warned Solidum.
PHIVOLCS also released tsunami safety and preparedness measures on their website:
- Do not stay in low-lying coastal areas after a felt earthquake. Move to higher grounds immediately.
2. If unusual sea conditions like rapid lowering of sea level are observed, immediately move toward high grounds.
3. Never go down the beach to watch for a tsunami. When you see the wave, you are too close to escape it.
4. During the retreat of sea level, interesting sights are often revealed. Fishes may be stranded on dry land thereby attracting people to collect them. Also sandbars and coral flats may be exposed. These scenes tempt people to flock to the shoreline thereby increasing the number of people at risk.
Solidum stressed the importance of community-based preparedness, built on planning and drills to create the following output:
- development of evacuation plans based on the hazard maps
- installation of different types of signage (signage for hazards, signage for the evacuation area, signage for the directions to go to the evacuation area)
- conducting of seminars and lectures
- drills
Tsunami preparedness during COVID-19
The devastation of several typhoons this year, coupled with the country’s location in the Pacific Ring of Fire, are proof that the Philippines is prone to various hazards. Because of the
COVID-19 pandemic, Solidum admitted that PHIVOLCS had to rethink their training methods. “Before, we actually go down to various coastal communities and conduct lectures in the evening, so that people who worked in the daytime can also attend. But the pandemic has enabled more people to listen because of the social media platform and our webinars. We’ve reached more people in terms of information campaign. But we hope that local government disaster managers will do the actual preparedness at the community level.”
Solidum noted that though COVID-19 continues to cause loss of lives and the disruption of public services, mobility and economic development, tsunami can create far more devastating impacts. “We will see the physical impacts through buildings, infrastructures, property, water supply pipes, electrical supply, communication system, roads, bridges, and ports. This is in addition to the physical impact on people because of the collapsing houses or the impact of the large volume of water. We have science, technology, and innovation from DOST that can help in preparedness and disaster risk reduction. We need to use it, but we need to share this information to the communities and the public,” he ended.
Watch the full press conference from PHIVOLCS.
Watch Panahon TV’s primer on tsunami.
In an effort to “build a kinder and more compassionate world,” the World Kindness Movement observes World Kindness Day on November 13 every year. It is “a day set aside to celebrate and appreciate kindness around the world.”
But how does one define kindness? This pandemic, simple acts of kindness like staying home and wearing a face mask can do a lot in curtailing the spread of the virus. Kindness can also mean getting to know something or someone beyond the general bias toward it—such as Wuhan City in Central China, which people all over the world now only know as the starting point of COVID-19. This World Kindness Day, we offer a different, kinder view of Hubei Province’s capital city.
It was once China’s capital.
From December 1926 to September 1927, Wuhan was the capital of the Kuomintang nationalist government. To create the new capital, China’s nationalist authorities merged the cities of Wuchang, Hankou, and Hanyang, from which Wuhan’s name was derived. However, the city lost its capital status when Chiang Kai-Shek established a new government in Nanjing.
It is directly related to the fall of Chinese monarchy.
The Wuhan Uprising in 1911 ended China’s last imperial dynasty, the Qing Dynasty. The success of the revolution prompted other provinces to follow, and in 1912, 18 more provinces united to form the Republic of China. The abdication of the Qing Dynasty the following month marked the end of the kingdom.

![]()
It is one of the world’s largest university towns and is a center for research.
With over one million students in 53 universities, Wuhan is considered one of the largest university towns in the world. It has 4 scientific and technological development parks, over 350 research institutes, and 1,656 high-tech enterprises.
It is referred to as the “Chicago of China.”
Chicago is a hub of transportation, which includes O’Hare, the most globally-connected airport in the US. Wuhan is similar in a sense that it offers transport to almost all parts of China. It is a center for ships and railways, with the Wuhan Railway Hub offering trips to major cities such as Beijing, Shanghai, Harbin, Chongqing, and Guangzhou.
Mulan probably lived in Wuhan.
Some theories state that Hua Mulan, the legendary female warrior and well-known “Disney Princess,” lived in the Huangpi District of Wuhan. Some even say that it is her birthplace.
Famous Places
Wuhan is a popular tourist destination with centuries-old attractions full of history, culture and astounding views.

![]()
Yellow Crane Tower
The Yellow Crane Tower was built in 223 as a watchtower for King Sun Quan’s army. The tower was destroyed and rebuilt seven times during the Ming (1368 – 1644) and Qing (1644 – 1911) Dynasties, and in 1884, it was completely destroyed in a fire.
Rebuilt in 1981, the Yellow Crane Tower stands 51.4 meters tall and consists of five floors. Interestingly, it appears the same regardless of the direction it is viewed from. Not only is it one of the most prominent towers in the south of the Yangtze River, it is also the symbol of Wuhan due to its cultural significance.
Hubu Alley
Built in 1368, Hubu Alley is known as “the First Alley for Chinese Snacks”, and has since been serving traditional Chinese breakfasts, such as hot dry noodles, beef noodles, Chinese doughnuts, and soup dumplings. From the Yellow Crane Tower, it can be reached 20 minutes by foot.

![]()
East Lake Scenic Area
The East Lake can be found on the Yangtze River’s south bank and in Wuchang’s east suburb. Covering an area of 87 square kilometers, it is the largest lake within a Chinese city. The area is “formed from many famous scenic spots along the bank,” and attracts many tourists due to its scenery.
Well-known Food and Dishes
Wuhan’s local food is said to be a mix of the cuisines of Sichuan, Chongqing, and Shanghai, which make it “spicy yet full of flavor.” Here are three of its most famous eats:
Hot Dry Noodles (Reganmian)
This is Wuhan’s most famous dish and the first one that locals will mention. The dish, which is essentially “dry noodles mixed with sesame paste, shallots and spicy seasoning,” is eaten for breakfast and as a snack.

![]()
Doupi
Often sold as a street snack, doupi’s layers are either made of tofu skin or “pancake lookalikes”. Glutinous rice is combined with usually no more than three ingredients chosen from beef, egg, mushrooms, beans, pork, or bamboo shoots stuffed in between the layers. Once everything is assembled, doupi is pan-fried, making it crispy on the outside and soft in the inside.
Mianwo
Though donut-shaped, mianwo is salty—made of rice milk, soybean milk, scallions and salt.

Wuhan’s Downside
Even with its must-see scenery and mouth-watering dishes, Wuhan, just like any other place, is not perfect.
Crowds and traffic jam
With a population of around 11 million, Wuhan has the densest population in Central China and is the 9th most populous city in the country. Large crowds, traffic congestions, and long lines are unavoidable in the city.
Before the East Lake became the picturesque spot that it is today, it suffered from soil, water, noise, and air pollution for decades. Wuhan used to be a major manufacturing site, causing the lake’s water quality to be very poor, with outbreaks of blue-green algae and dead fish. However, through the years, its water quality has dramatically improved. Because of this, East Lake is now able to host swimming contests, and serves as one of the best attractions in the city.
Waste concerns
In 2019, street protests were carried out in Yangluo of the Xinzhou District by around 10,000 local residents rallying against the construction of the Chenjiachong waste-to-energy plant – an incinerator that the government planned to construct to handle the city’s waste. But the incinerator was said to emit cancer-inducing toxins, and was going to be built only 800 meters away from residences.
The Xinzhou District government tried to calm protesters down by assuring them that their voices will be heard in the decision-making process. However, reports said that government officials and the police went door-to-door to force residents to sign the project’s consent form, threatening them if they refused to do so.
From its cultural and historical prominence to its contributions to technological innovation, there is clearly more to Wuhan than just the coronavirus. Like any other city, it has its strengths and imperfections worth learning about especially during the pandemic and World Kindness Day.
The pandemic’s global economic impact is undeniable. According to a World Bank publication last June, the world’s gross domestic product (GDP), which determines economic health, is forecast to contract by 5.2%. Meanwhile, the Asian Development Bank predicts the Philippine economy to shrink by 7.3% this year.
Filipino employees suffered, with 46% of them—equivalent to more than 27 million—losing their jobs during the pandemic, according to the Social Weather Stations (SWS) survey.
With people scrambling to survive and earn a living, we gathered wise words from a sector of society that used to get the short end of the financial stick, but through the years, have proven their monetary smarts—the women.
Pinay Financial Power
For centuries, women all over the world have been deprived of opportunities for education, political empowerment, health and economic development. But in recent years, Filipino women have been faring better. According to the World Economic Forum’s Global Gender Gap Reports in 2017, the Philippines was the only Asian nation and developing country included in the top 10 countries that promoted gender equality.
An article from the Alliance for Financial Inclusion considers culture as a driving force for female empowerment. In the Philippines, household budgets and finances are usually managed by the women. Interestingly, in 2012, the Philippine Statistics Authority reported that female-headed households enjoyed an income of 1.2% more than the households led by men, the former having annual savings of 3.2% more than the latter. In 2008, the Functional Literacy, Education and Mass Media Survey stated that financial literacy among Filipino women is higher (88.7%) than the men’s (84.2%).
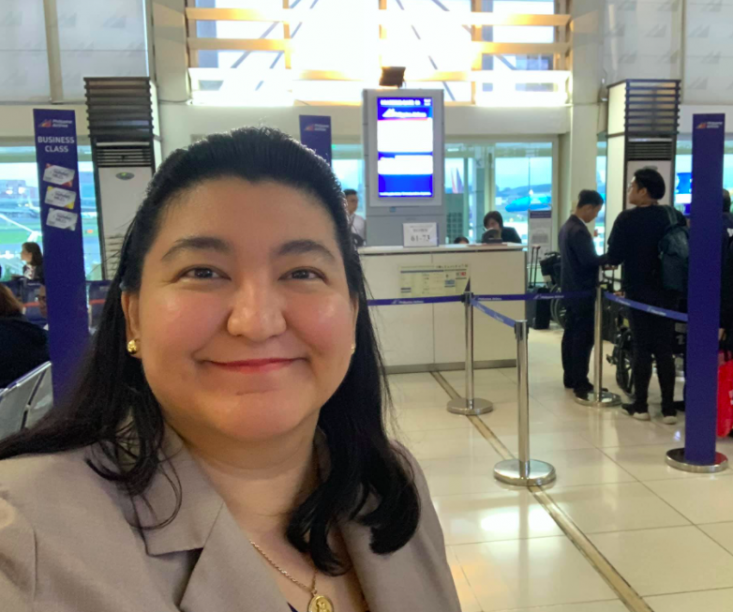 Deliza leaving for a business trip a year before the pandemic
Deliza leaving for a business trip a year before the pandemic
Hit by the Pandemic
Since 2004, Deliza Ridoloso has been managing a successful products-and-services business that caters to the banking industry. “Before COVID-19, we were reaching the height of our consolidated revenues,” she shares. “When ECQ [enhanced community quarantine] hit, we lost 85% of our revenues. At least we had 15% left; it was better than nothing. But getting that 15% was a lot of hard work.”
For Lala Javier-Rosales, mother of two, the pandemic was a wake-up call. As the one in charge of dispatching foreign volunteers for a Japanese governmental agency that provides assistance in the Philippines, she feared for her job. “Since all the volunteers were recalled because of the pandemic, I thought my employers would let me go. But the agency’s president assured us that we would keep our jobs.” Though she was retained, Lala realized that nothing was ever really certain. “Before, I felt so secure in my job. I earned decent pay, and I was planning to rely on my work until I retired. But now, I realize that I need to be prepared for unplanned situations.”
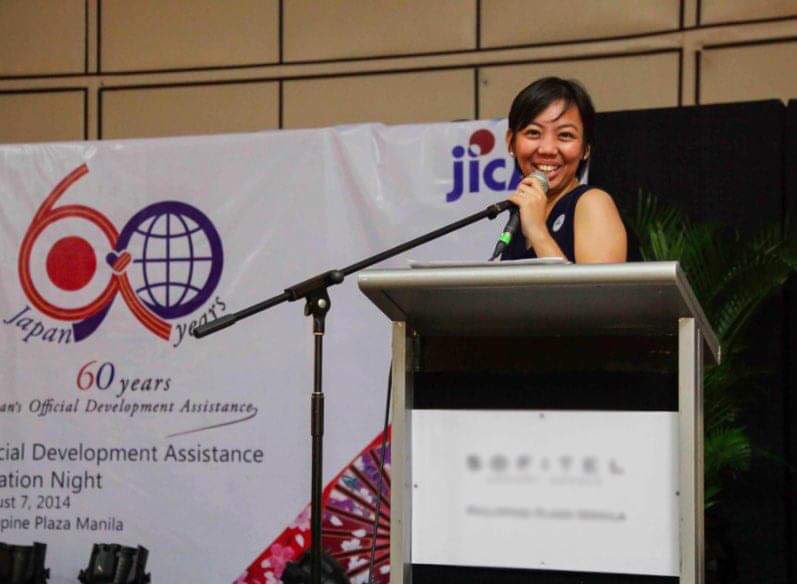 Lala hosting a company event
Lala hosting a company event
Rapid Adjustment
Deliza’s company managed to continue operations despite the changing quarantine categories in Metro Manila. This, Deliza attributes to their business continuity plan, which the management team began back in 2008. “Our business continuity plan was for earthquakes and floods, and not really a pandemic. But because we were already getting news of the virus in January, and started hearing of lockdowns in other countries, we started tweaking our plan.”
Deliza admits that back then, they didn’t know that a pandemic was about to happen. Still, they held emergency meetings twice a week to prepare for the virus in case it hit Manila. “For more than a decade, we’ve been saving documents in cloud storage and an off-site server. What we prepared for at that time was for disasters like earthquakes and fires. But the plan was also applicable when ECQ was declared and we couldn’t get to the office.” The plan also included protocol for people working from home, and health monitoring. “From the beginning, we already made our own health checklist based on information from WHO (World Health Organization).
Because Deliza’s company offers business-to-business products, they beefed up their remote marketing strategy. “This was where our 15% revenues came from. We had to adapt right away. We did video conferencing. Because we couldn’t meet face-to-face with our clients, we had our presentations on Zoom. We worked on our digital marketing to make sure our presentations were clear. Communication was important— with our clients, our staff, our suppliers.” Her management team met as often as twice a day via Zoom. “The situation kept on changing at the end of the day. When I think about it now, it sounds a little excessive? But it wasn’t because we were working so hard to continue operations remotely. We had to re-engineer our processes.”
At the start of the lockdown, working from home allowed Lala to re-assess her family’s finances. “I had time to reflect. Before the pandemic, I had an essential oils business that I wasn’t really taking seriously. From time to time, I’d share about it on my Facebook page, but I wasn’t conscientious about it.” Since the pandemic, Lala has become more vocal and intentional about her business. “I truly love essential oils, and the more I shared about it, more people signed up under me until my business grew. It came to a point where I started earning more from it than from my day job.”
Another earning opportunity came to Lala because of her love for food. “Food is my stress-reliever. And because me and my husband hail from Batangas, we found ourselves missing the delicacies there.” When the couple secured a travel pass, Lala offered to buy Batangas delicacies for her interested friends. “I’d post the announcement and food photos on my Facebook wall. That side business augmented our family income. It was a great feeling to make other people happy through food.”
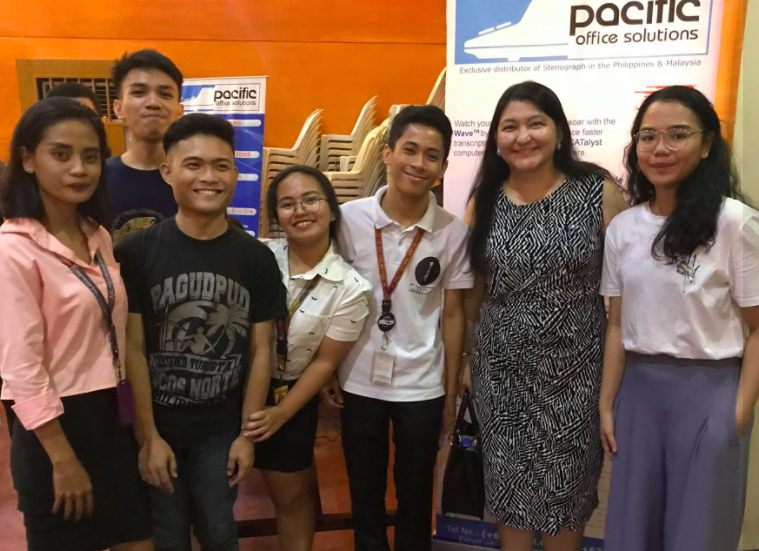 Deliza (2nd from right) with university students
Deliza (2nd from right) with university students
Present Scenario
Up until June, Deliza’s company managed to keep all their approximately 100 employees. But eventually, some were let go. “We tried to give them the best arrangement we could afford. We allowed them to use up their sick and vacation leaves so they’d still get paid. One of our managers who was a senior citizen got the retirement package, which we give in monthly installments.”
Revenues have picked up in September, but Deliza says cash flow continues to be tight. To keep other employees, their work hours were cut down, along with their pay. “At the end of the year, we aim to break even at the minimum. We’re trying our best to keep all our people and not have any more layoffs. So we’re trying to keep costs covered while operating as best as we can.”
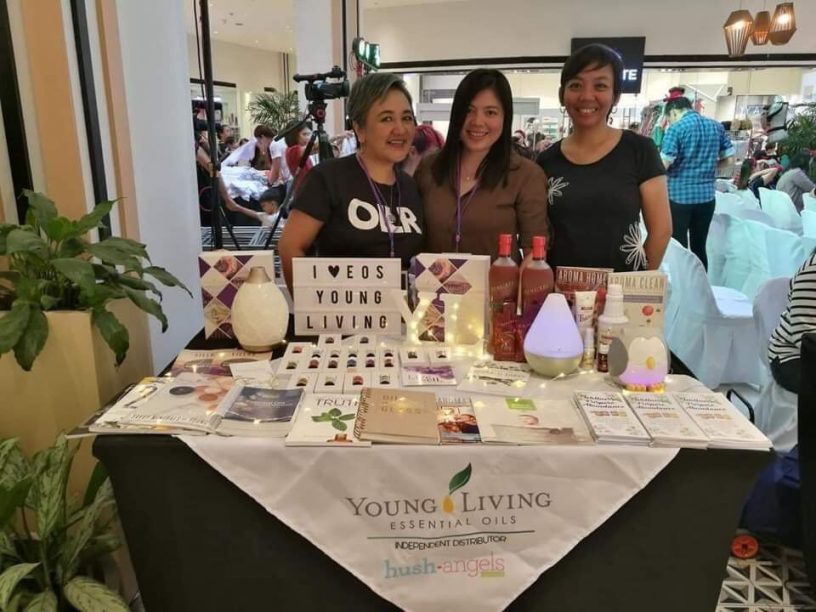 Lala (right) and her essential oil business
Lala (right) and her essential oil business
Financial Survival Tips
Survival depends hugely on preparedness. Deliza and Lala share the insights they have gathered during the pandemic.
Be informed. “Being aware of global current events gave us an idea of what’s going to happen in case Manila was put under lockdown. Being on top of the news is very important,” says Deliza. “We were being observant, and prepared in our own way.”
Never be complacent. Because of the pandemic, Lala learned that it’s vital to have multiple income streams. “Aside from side businesses, my husband has also become more involved in their Batangas farm. We want to grow our own food, and maybe eventually, earn from it.” In choosing side businesses, Lala advises to “find something you’re passionate about. Turn your passion and talent into something income-generating.”
Work on a business continuity plan. “I believe that every business should have a continuity plan in case of emergencies,” says Deliza. “It’s a lot of work because it has to tailor-fit your operations. It’s not a template you can pull out a book; you have to make it your own. Every year, we refine our business continuity plan.”
Maintain a good relationship with banks. “We have bank loans, and luckily, we’re able to meet our responsibilities with them. If you can’t pay them, then you shouldn’t run. You need to talk to the banks, and discuss what you can do.” Deliza also shares her company’s golden rule: Don’t borrow money for something consumable. “We make loans to make purchases for our goods we plan to sell, not those we already sold. We borrow money to make money, so we can pay back our loans.
Set goals. Outlining goals is also a sign of preparedness. “Our team talks about our financial goals, about what we need to target to keep as many people as we can, and keep the company healthy.” Lala’s latest goal is to secure a critical-health insurance for her family. “My father-in-law was recently hospitalized and he shelled out a huge amount of money. If that were to happen to my family, I wouldn’t know where to get the cash.”
Gain support. While Lala’s network of friends was instrumental in growing her side businesses promoted through social media, Deliza finds that being part of a business organization helped validate her company’s steps in surviving the pandemic. “Being part of a business group helped boost my confidence and knowledge on how we should do things. It gave me a better understanding of best practices.”
The pandemic may be far from over, but these women will continue to do their best to weather the financial storm. “I have no plans of resigning, and I aim to further grow my businesses,” Lala declares. Deliza stresses the importance of taking the time to prepare for possible outcomes. “If you’re leading your company, you should have a clear vision. You need to go to a quiet place and meditate and think about scenarios. You really need to adapt if you want your business to survive.”
Managing the rainy season this year is vastly different from the previous ones as the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) continues to pose threats on the country’s public health, economy, and environment. During this time, tropical cyclones, combined with the enhanced southwest monsoon (habagat), are expected to bring floods, storm surges, destructive winds, and landslides which may hamper efforts in curtailing the spread of the virus. According to the Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration (PAGASA), 6 to 10 cyclones may enter the Philippine Area of Responsibility (PAR) from July to August. Additionally, there is a 50% chance that La Niña may develop in the last quarter of the year, bringing wetter conditions in the eastern section of the country.
 Typhoon Season. Two tropical cyclones have traversed the PAR since the first COVID-19 case in Manila on January 30. Typhoon Ambo, internationally known as Vongfong, made landfall six times on May 14 and 15, while Tropical Depression Butchoy hit the landmass twice on June 11. Both pummeled the coronavirus-stricken Luzon.
Typhoon Season. Two tropical cyclones have traversed the PAR since the first COVID-19 case in Manila on January 30. Typhoon Ambo, internationally known as Vongfong, made landfall six times on May 14 and 15, while Tropical Depression Butchoy hit the landmass twice on June 11. Both pummeled the coronavirus-stricken Luzon.
Aylen Labiano, who has been selling agricultural products beside an ecotourism road in Lucena, Quezon for nearly a year now, recounts in Filipino how Bagyong Ambo impacted her livelihood. “The recent cyclone devastated vegetation and banana trees, which prompted suppliers and sellers to raise prices. But people want low-cost food since a lot of them lost their jobs, and the situation has not yet normalized. If typhoons continue to ravage our livelihood, we will not be able to make ends meet.”
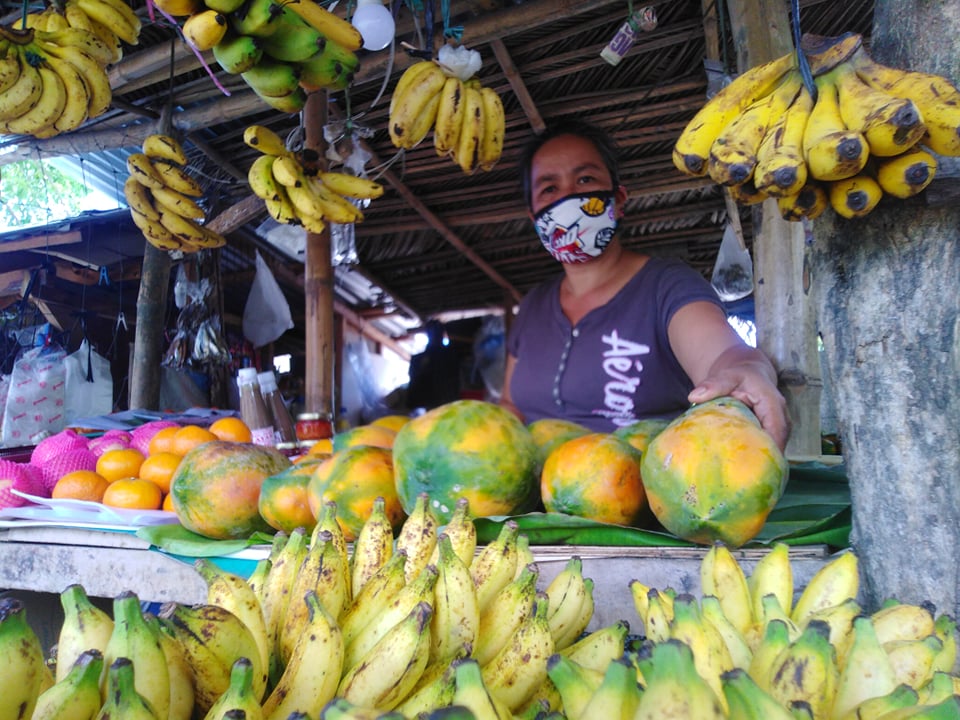 Agricultural Uncertainty. Agricultural loss due to Typhoon Ambo is estimated at Php1.37B.
Agricultural Uncertainty. Agricultural loss due to Typhoon Ambo is estimated at Php1.37B.
19-year old Carl Ian Pedregosa from San Francisco, Quezon shares how his family monitored the news to prepare for the typhoon. “But when the rains arrived, we experienced power outage, which lasted for more than a week. Some coconuts, which were supposed to be extracted for oil, also fell during the storm. We fed them to the hogs instead.” Pedregosa also worries about how power interruptions can not only make it difficult for his family to stay updated, but also disrupt his education in the coming school year, especially with academic institutions planning to utilize online learning.
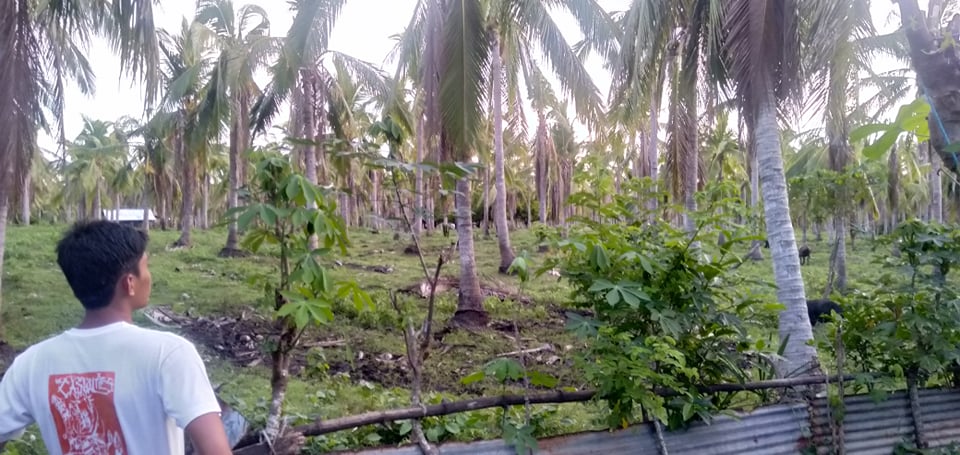 Felled coconut trees in Quezon Province, one of the top agricultural producers of copra in the country.
Felled coconut trees in Quezon Province, one of the top agricultural producers of copra in the country.
 PAGASA Cyclone Forecast
PAGASA Cyclone Forecast
Overwhelming Complications
While studies say that rain may help dilute the virus on contaminated surfaces, it also favors other diseases that may strain our healthcare system.
 Monsoon Diseases. With the rains comes a downpour of diseases, ranging from the easily curable, such as diarrhea and cough, to the downright deadly, including leptospirosis and typhoid fever. Meanwhile, the World Health Organization (WHO) clarifies that there is still no evidence supporting the possible transmission of COVID-19 through mosquitos and houseflies. To date, no peer-reviewed studies have proven that the ongoing seasonal change has weakened the potency of the virus, and if it can interact with other viruses to develop worse symptoms.
Monsoon Diseases. With the rains comes a downpour of diseases, ranging from the easily curable, such as diarrhea and cough, to the downright deadly, including leptospirosis and typhoid fever. Meanwhile, the World Health Organization (WHO) clarifies that there is still no evidence supporting the possible transmission of COVID-19 through mosquitos and houseflies. To date, no peer-reviewed studies have proven that the ongoing seasonal change has weakened the potency of the virus, and if it can interact with other viruses to develop worse symptoms.
But the real problem lies with how symptoms of monsoon diseases are almost similar to those of COVID-19’s. “Whether people tested positive or negative for COVID-19, we will need to test them for other possible diseases which will make the process longer,” states Dr. Generoso Roberto of the Philippine Society of Public Health Physicians (PSPHP).
The Department of Health (DOH) targets to license 65 COVID-19 testing laboratories by the end of July to test 1.5 to 2% of the population. To date, there are 62 accredited labs with a rated testing capacity of 50,000 daily, prioritizing suspect cases, individuals with travel history, and healthcare workers with possible exposure, whether they are symptomatic or asymptomatic. However, there is still a gap between rated and actual capacity with 12,000 to 16,000 people tested a day due to manpower and supply chain issues— problems that arise globally.
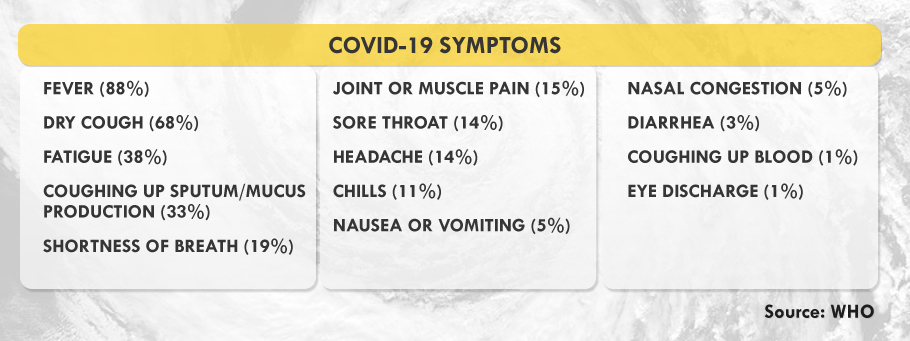 Confirmed Symptoms. The United Kingdom has included anosmia, or loss of taste or smell, as a predictor for COVID-19. Experts say that patients infected with COVID-19 usually transmit the disease before their symptoms manifest, their ability to infect peaking until the third day after symptoms start showing.
Confirmed Symptoms. The United Kingdom has included anosmia, or loss of taste or smell, as a predictor for COVID-19. Experts say that patients infected with COVID-19 usually transmit the disease before their symptoms manifest, their ability to infect peaking until the third day after symptoms start showing.
“We also need to plan where we’ll be admitting patients diagnosed with other diseases if certain hospitals are designated as COVID-19 treatment sites,” Dr. Roberto explained. Meanwhile, people living in rural areas, especially in remote islands, will face the challenge of transporting patients and doctors to the barrios during the typhoon season. “This means that patients can develop severe symptoms by the time they’re brought to healthcare facilities,” Dr. Roberto explained.
Though virtual healthcare seeks to keep patients at home, the system is not inclusive of, and accessible among the marginalized. According to the Speedtest Global Index, upload and download speeds for mobile and fixed broadband in the country are still below the global average. The Social Weather Stations (SWS) also shows that only 22.4% of Filipino families in the country owns a personal computer at home.
Rising Tide of Vulnerabilities
The country is still on its first wave of COVID-19 cases when the government gradually eased quarantine measures, allowing some businesses to reopen. Though this move aims to save the economy from socioeconomic impacts, such as unemployment and hunger, it may also worsen, not only the health crisis, but also disaster risks.
“We need to do scenario building or disaster imagination so we can prepare for complex emergencies,” says Science and Technology Undersecretary Renato Solidum, Jr. in Filipino. Government and private sectors should have continuity plans for their public service and businesses since the pandemic may coincide with hazards that often transpire in the country, such as earthquakes, tsunamis, and volcanic eruptions.
On March 11, days before the Enhanced Community Quarantine (ECQ) in Luzon, volcanologists placed Mount Kanlaon in Negros Island under Alert Level 1, prohibiting people around its 4-kilometer-radius danger zone for possible sudden phreatic eruptions. A series of volcano-tectonic quakes has been observed since June 21. Meanwhile, Mayon Volcano has been under Alert Level 2 since March 2018.
Urbanized cities are highly exposed both to the pandemic and the negative impacts of natural hazards due to their dense structures and population. According to Solidum, the government’s Balik-Probinsya program may be a good solution to decongest cities as long as comprehensive safety protocols are strictly employed. This program, institutionalized through Executive Order No. 114, seeks to encourage people, especially the informal settlers, to return to their home provinces.
Metro Manila, considered as the seat of government, is no exception to looming catastrophe. Here lies the biggest portion of the West Valley Fault (WVF), an active earthquake generator traversing Bulacan, Quezon City, Marikina, Pasig, Taguig, Muntinlupa, Rizal, Laguna, and Cavite. These areas are part of the Greater Metro Manila Area (GMMA), a megacity with an estimated population of 20 million. About 35% of its populace are informal settlers, many of them living below poverty line.
WVF’s massive earthquakes occur every 400 to 600 years. Its last movement that caused a magnitude 5.7 quake was in 1658 or 362 years ago. According to a joint study by Australia and the Philippines, the fault’s next movement may produce a magnitude 7.2 earthquake, resulting in 34,000 deaths due to collapsed buildings—and an additional 18,000 fire-related fatalities in the metropolis. Furthermore, infrastructures, lifelines, and about 40% of residential buildings are likely to be heavily or partially damaged, causing 2.3 trillion pesos worth of damage. The management of such a huge disaster requires close coordination, which the current pandemic hampers.
If protocols are not properly implemented and followed, evacuation centers during disasters coupled with monsoon diseases may be a breeding ground for more health risks. A person with COVID-19 may infect dozens of people, including Disaster Risk Reduction and Management (DRRM) officers who are on the frontline during rescue and relief operations.
One of which is Alex Pimentel, a DRRM officer in Batangas City, who tested positive for the disease in April. “Parang nandidiri ang ibang tao sa community, lalo na when I tested positive,” he shares. (When I tested positive, people in the community avoided me like the plague.)
DRRM offices help by providing transportation for COVID-19-related patients, manning centers for Persons Under Monitoring (PUM), and disinfecting public spaces, among others. But if a natural disaster strikes, people like Alex will even have a more difficult time doing their duty. “It will be hard for the DRRM frontliners responding with merged Search and Rescue and COVID-19 personal protective equipment. We also worry about funds because we’ve already spent so much during the Taal eruption, assisting 11,000 evacuees, followed by the pandemic response.“
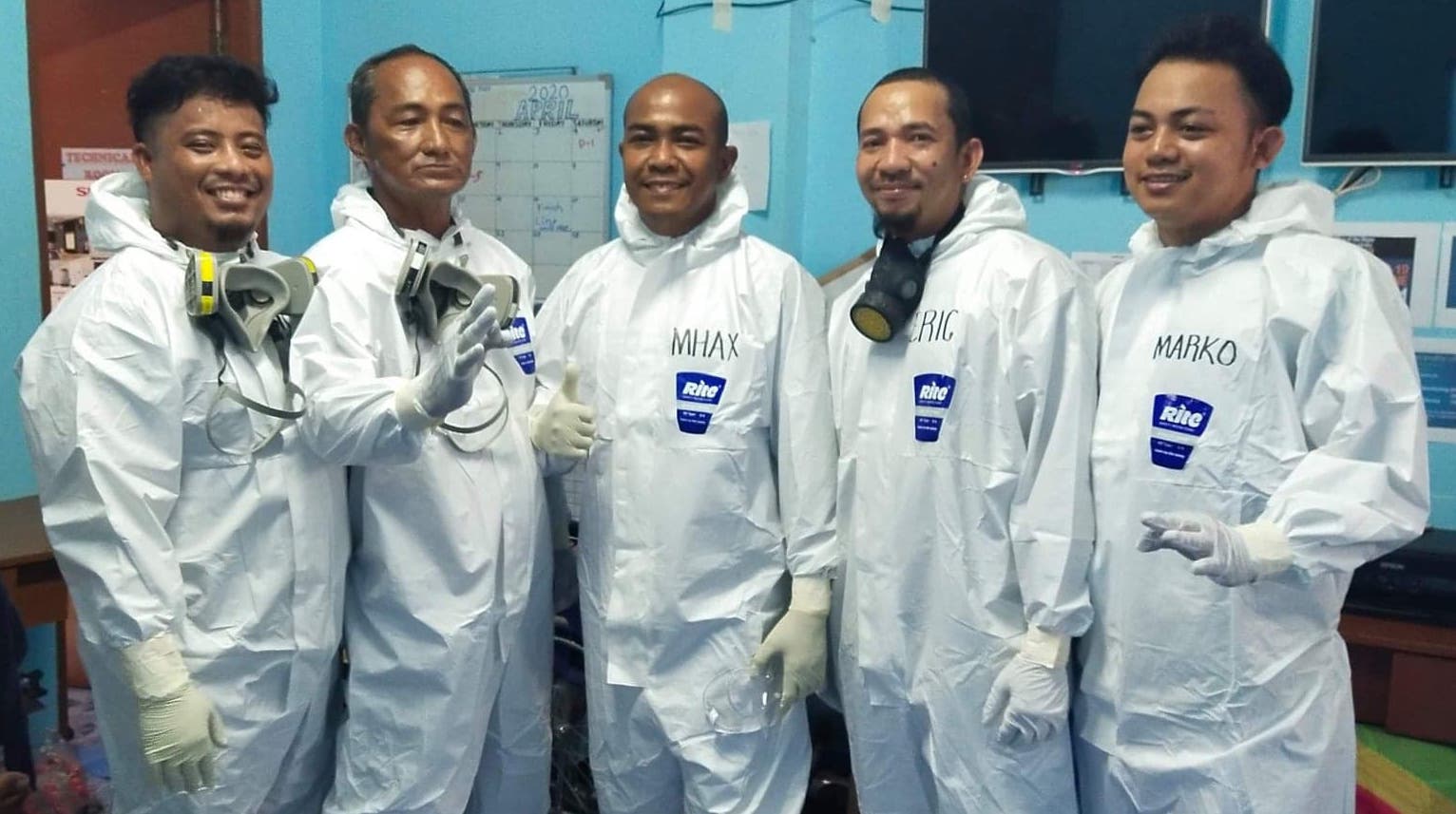 Nasugbu, Batangas LDRRMO
Nasugbu, Batangas LDRRMO
The Need for Disaster Imagination
Solidum explains that disaster imagination means preparing for worst-case scenarios and their possible impacts. “People and the Local Government Units (LGUs) should know the hazards in their areas so they can plan appropriately. What if an earthquake transpires? What are its impacts? Have we identified the vulnerable population? Where are we bringing them?”
A study conducted by the International Organization for Migration (IOM) in 2014 exposed that more than 90% of evacuation sites in Eastern Samar were partially or completely devastated during the onslaught of Typhoon Haiyan, locally known as Yolanda. These were churches, schools, and community centers, which were identified by LGUs as safe.
On June 13, the Office of Civil Defense (OCD) provided LGUs with guidelines so they can meet the health standards of the COVID-19 National Task Force in conducting online Pre-Disaster Risk Assessment. This allows LGUs to prepare their inventory of resources, logistical requirements, relief packs, and evacuation centers. “If we conduct pre-emptive evacuation, we see to it that everybody is protected. We should be observing social distancing and we limit the number of people in the evacuation centers. We also see to it that our responders are protected,“ says OCD’s Operations Service Director Harold Cabreros.
Risk Management during the Pandemic
The Philippine Institute of Volcanology and Seismology (PHIVOLCS), PAGASA, and the Mines and Geosciences Bureau (MGB) have developed Hazard Hunter, a tool that Filipinos can use to assess seismic, volcanic, hydrometeorological, and climatological hazards in their locations. It is free and readily- available online, especially useful for property owners, buyers, land developers, planners, and other stakeholders.
It is also important to know what to do before, during, and after several natural hazards.
 Graphics by Jearom Andre Martinez
Graphics by Jearom Andre Martinez
This global crisis is not just about adapting to changes, but also preparing for complex emergencies. With inclusive, sustainable solutions, everyone—even the weakest—can be empowered to rise up to the challenges.
Assistance and additional reports from: Fritzjay Labiano, Relly Bernardo (Antipolo PIO), Vic Simoun Montoso, Mark Cashean Timbal (OCD), Lilia Malabuyoc (OCD)
Disasters strike like thieves in the night, unpredictable and dangerous. In a span of six days, they’ve wreaked havoc in different parts of the world, including the Philippines.
Sinkhole in Downtown Fukuoka
On November 8, a giant sinkhole ripped a busy road in the southwestern stretch of Fukuoka, Southern Japan. The 15-meter-deep sinkhole spanned 30 meters—
roughly half the size of an Olympic swimming pool. Though not a single person was injured, it caused interruptions in water, power, telecommunications and gas supply in some parts of the city. Residents speculated that the nearby subway construction might have triggered the slumping of the 5-lane thoroughway, but civil engineering experts attributed it to the soil’s composition, which is mostly sand.

Japan proved its efficiency in crisis management as sewage pipes and utility lines in the business district were restored in just two days. Nearly a week later, the collapsed road was repaired with a mixture of sand and cement, making it 30 times stronger than it used to be. On November 15, pedestrians and vehicles started using the re-opened street.
Quake in New Zealand
On November 13, a powerful 7.8 magnitude quake hit New Zealand’s South Island—the strongest in the region since 1929. Tsunamis towering up to 8 feet followed minutes after the groundshaking. These inundated communities in Kaikoura, a coastal town near the city of Christchurch. “This is the highest tsunami wave that New Zealand has seen in at least 38 years,” said Weather Watch New Zealand. According to experts, the tsunamis could have been more catastrophic if these transpired during high tide. Luckily, tide level was low at that time.
Apart from homes, livelihoods, office buildings and transport routes reduced to rubble, two fatalities in Canterbury were also reported. “In the short term, what we’re trying to do is to make sure that people of Kaikoura and the like have food, water, help and backup,” NZ Prime Minister John Key said.

No less than 40 aftershocks were recorded, but the strongest was a magnitude 6.2, which occurred a few hours after the major quake.
The 2016 Kaikoura quake has less death tolls than the massive 6.3 magnitude quake that struck Christchurch in 2011, causing 185 fatalities.
An average of 15,000 quakes per year are recorded in New Zealand, but about 150 are strong enough to be felt. The country is situated in the Pacific Ring of Fire, a horseshoe-shaped region where the most number of quakes and volcanic activities transpire.
On the same day, a 6.2 magnitude quake rocked Northwestern Argentina. The epicenter was recorded in the La Rioja province, but tremors were also felt in Catamarca, Tucuman, and Cordoba. However, these caused no damage and injuries.
Know how to prepare for huge quakes:
Volcano Erupts in Mexico
Western Mexico’s Colima Volcano, also known as the Volcano of Fire displayed unusual seismic activities, which prompted the evacuation of hundreds of people earlier this year. After a few months, this volcano erupted, forcing similar evacuations last October.
But last November 15, Tuesday, the abnormal activity of the volcano slowly increased as the new lava dome in its summit crater continued to grow. Its lava flow, rock fall, glowing avalanches and ash fall posed a threat to locals.

Colima Volcano has an elevation of nearly 4,000 meters with a 5-kilometer-wide crater mouth. 30 eruptions have been recorded in the past 431 years. It is considered one of the most active and dangerous volcanoes in Central America.
Know how to prepare for volcanic eruptions:
Mandaluyong faces State of Calamity
Three people died as 500 houses were burned down in an 8-hour blaze in Mandaluyong City on November 13, at around 7:45 pm. The fire consumed sections of two densely populated and fire-prone barangays. The Bureau of Fire Protection traced the cause to a leaking gas tank, and estimated property loss at 10 million pesos.

1,465 families from Barangays Addition Hills and San Jose were left homeless. Some have evacuated to a covered court and two elementary schools. The local government promised to provide financial assistance to the displaced families, and help them reconstruct their homes or move to new residences. P8,000 shall be given to families who lost their abodes; home sharers shall receive P5,000; while families who were renting would get P3,000.
On November 15, another fire incident transpired in Barangay Addition Hills—the fifth in the area for this year.
Here’s how you can prevent loss of lives and property due to fire especially this holiday season:

After the scorching heat of the previous months, rain showers and thunderstorms are now taking center stage. Apart from risks to our health, the rainy season also poses threats for those on the road.
Driving is more dangerous in heavy downpour, especially at night. To help ensure your safety, here are some tips:

SLOW DOWN
Roads are more slippery when wet. Remember that there should be a four-second interval in between cars, so avoid tailgating or driving too close to the car in front of you. This helps avoid accidents, giving you enough time to brake or take action in case the car in front of you suddenly stops or swerves.
TURN WIPERS ON
Before you drive, ensure that your wipers and washer systems are functional. Front visibility can be hampered by hard rubber on old wipers, while dysfunctional washers that are unable to effectively clean the windshield can distort the view. Replace wipers regularly or at least once a year.
YES TO HEADLIGHTS
According to Autoindustriya.com, turning the headlights on does not improve your vision during rains, but increases your car’s visibility to traffic. This way, the drivers behind will be able to gauge their distance from you.
NO TO HAZARD LIGHTS
Hazard lights limit, not only your vision, but also that of drivers of the cars adjacent to you. These flashing lights, which can be very distracting, should only be used during emergencies or when you want to warn others that your vehicle has become a road hazard.
KNOW THE TERRAIN
It pays to familiarize yourself with your destination—not only with directions on how to get there, but also the location’s topography. Being informed about choke points and flood-prone areas can help divert you from danger and wasted time. If you are driving within Metro Manila, check out MMDA’s (Metropolitan Manila Development Authority) list of more than 80 flood-prone areas to avoid during a heavy downpour. Get the complete list: https://www.facebook.com/Panahon.TV/photos/?tab=album&album_id=1120283194682184


Take caution in driving through moving water especially if the ground is totally obscured. Stop the car before entering the flooded area and check the water level. If the water is deeper than the bottom of your doors or the bottom third of your wheels, attempting to drive through it might damage your electronic control systems. Look for a detour instead.
WATCH OUT
Road hazards are much harder to see at night. Watch out for road hazards such as open manholes, street diggings, humps and gullies. Aside from these, be aware of pedestrians or commuters. During rains, pedestrians carry umbrellas, which might limit their vision, causing them to overlook your vehicle.
HIT THE BRAKE & HAVE A BREAK
If you have problems with visibility or if you’re feeling uncertain about the road or terrain, find a safe place to park for a while. Learn to wait until the rain stops and for the flood waters to subside. Sometimes, it’s better to wait than to risk your vehicle and safety.
MONITOR THE WEATHER
Chances of rain, expected temperature, thunderstorms and flood alerts – being informed about these can save you. Knowing what the weather will be like within the next 24 hours will give you an idea on how traffic will behave throughout the day.
If the weather is really bad, think twice about going out. If not, it’s better to stay home and be safe rather than expose yourself to harm.
Sources:
Autoindustriya.com
www.telegraph.co.uk
www.smartmotorist.com
Surrounded by bodies of water, the Philippines sits astride the typhoon belt. Each year, an average of 19 to 20 tropical cyclones or bagyo enters the Philippine Area of Responsibility (PAR), with 8 to 9 of these crossing the landmass.
In 2014, 19 tropical cyclones were recorded to have entered PAR. Two of them were experienced before the year ended, making their respective landfalls in the Visayas and Mindanao areas.
Bagyong Ruby

Since its development from a low pressure area on the last day of November, major weather agencies across the globe closely monitored the potentially dangerous typhoon, later given the international name Hagupit.
Filipinos were alerted against the threat of the approaching cyclone as early as December 2, even if Hagupit was still too far to affect the country.
Entering PAR on December 4, the cyclone was locally named Ruby. Two possible scenarios were presented: for it to 1) make landfall and 2) recurve. Despite hoping for the latter, Ruby crossed the archipelago, hitting the land five times before exiting PAR by the evening of December 10.
During its course on land, Ruby left 18 dead and 916 injured. Over 5 billion pesos in damages to agriculture and infrastructure were also reported.
With the catastrophe endured by Filipinos in November 2013 caused by bagyong Yolanda, the Philippines may have learned its lesson. A lot of it, it seems, were applied during the preparations for Ruby.
No less than President Benigno Aquino III ensured that each agency’s preparations were already in place before Ruby’s arrival. This included quizzing his cabinet secretaries on their efforts in preparation for Ruby, to avoid a repeat of the Yolanda situation. A meeting in Camp Aguinaldo was held to mitigate the impact of Ruby in the following days.
Agencies also layman-ized the terms and phrases used in order to make sure everyone understood and acted accordingly. Continuous dissemination of weather bulletins, the initiation of pre-emptive evacuation, and other precautionary measures were undertaken as early as December 2 when the typhoon was still outside the PAR.
BAGYONG SENIANG
Right after Christmas up until New Year’s, PAGASA weather forecasters dutifully monitored the last tropical cyclone of the year— Seniang.
Dumping heavy rains that caused widespread flooding and landslides, among others, Seniang made landfall four times before leaving the PAR on the 2nd of January.
Aside from the 65 deaths, 41 injuries and 7 missing persons, Seniang also caused damages of more than 758 million pesos as of press time.
With the death toll significantly higher compared to Ruby, criticisms were thrown at the government for “falling short in its preparations” for the onslaught of bagyong Seniang. However, Malacañang refuted these claims saying that the government’s preparations and response were comprehensive. Citing the latest report from the National Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Council, Presidential Communications Operations Office Secretary Sonny Coloma stated that many of the casualties came from isolated cases of landslide and flashflood incidents, in areas that were not “designated as danger zones.”
LESSONS LEARNED
A weather disturbance often takes a few days before it develops into something massive. State meteorologists monitor this through weather satellites, enabling them to alert the public and give them ample time to prepare before a bagyo strikes.
Over the years, the Filipinos have endured the countless devastating effects of cyclones with rising death tolls and damages headlining the news. Though we can’t stop a cyclone from forming, we can minimize its disastrous impact. By focusing on disaster mitigation and preparedness, we help curb the overwhelming consequences of a calamity.
Arm yourself with some weather wisdom.
What is a thunderstorm? A low pressure area? The most dangerous part of a bagyo? (The eye wall, fyi.) Knowing these relevant weather terms help us understand forecasts better, which help us prepare for the coming weather disturbances.
Monitor weather updates.
Nowadays, information comes easily through various platforms—the television, radio, and the Internet. With real-time updates and lead-time forecasts, disaster preparedness is within our reach.
Have an emergency kit.
We can’t stress this enough. Emergency kits save lives. Prepare emergency kits ahead of time and store them in accessible areas so you can easily find them when the need arises.
Make emergency plans with your family.
When disaster strikes, family members may get separated. Make sure the whole family is prepared and informed on crucial information, such as emergency exits, meet-up points, and ways to contact each other. In line with this, it’s also important to know the emergency hotlines in your area.
Identify the threats on your property.
Is your area prone to flooding? Can a storm surge reach your house? Is your area mountainous and prone to landslides? If you are living in a hazard-prone area, evacuate as early as possible. Otherwise, stay inside the house and keep calm.
Store enough food and water.
The movements of tropical cyclones are not definite. Some move speedily; others start fast then slow down later on. Business operations may take time to resume after a disaster so better make sure your supplies will last for a few days.
Heed the advice of local authorities.
If you’re asked to evacuate, do so and be sure to follow instructions. Before leaving, turn off all utilities and secure your home. After the disaster has passed, return home only when officials have deemed it safe.
Are you ready for future disasters? Be informed, prepared, and safe! See below the names that will be used for tropical cyclones that will enter the PAR this 2015






